Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Industry
refers to the material production sector
which is engaged in extraction of natural resources and processing and
reprocessing of minerals and agricultural products, including: (1) extraction
of natural resources, such as mining, salt production (but not including
hunting and fishing); (2) processing and reprocessing of farm and sideline
produces, such as rice husking, flour milling, wine making, oil pressing, silk
reeling, spinning and weaving, and leather making; (3) manufacture of
industrial products, such as steel making, iron smelting, chemicals
manufacturing, petroleum processing, machine building, timber processing; water
and gas production and electricity generation and supply; (4) repairing of
industrial products such as repairing of machinery and means of transport
(including cars).
Prior to 1984, the rural industry run by
villages and cooperative organizations under village was classified into
agriculture. Since 1984, it has been grouped into industry. Units of industrial
statistics survey corporate industrial enterprises with independent accounting
system.
Corporate industrial enterprises with
independent accounting system refer to enterprises engaging in industrial
production activities, which meet the following requirements: they are
established legally, having their own names, organizations, location, able to
take civil liability; they possess and use their assets independently, assume
liabilities, and are entitled to sign contracts with other units; they are
financially independent and compile their own balance sheets.
Light
Industry
refers to the industry that produces consumer goods and hand tools. It
consists of two categories, depending on the materials used: (1) Industries
using farm products as raw materials. These are branches of light industry
which directly or indirectly use farm products as basic raw materials,
including the manufacture of food and beverages, tobacco processing, textile,
clothing, fur and leather manufacturing, paper making, printing, etc. (2)
Industries using non farm products as raw materials. These are branches of
light industry which use manufactured goods as raw materials, including the
manufacture of cultural, educational articles and sports goods, chemicals,
synthetic fiber, chemical products for daily use, glass products for daily use,
metal products for daily use, hand tools, medical apparatus and instruments,
and the manufacture of cultural and clerical machinery.
Heavy
Industry
refers to the industry which produces capital goods, and provides various
sectors of the national economy with necessary material and technical basis. It
consists of the following three branches according to the purpose of production
or the use of products: (1) Mining, quarrying and logging industry refers to
the industry that extracts natural resources, including extraction of
petroleum, coal, metal and non-metal ores. (2) Raw materials industry refers to
the industry that provides various sectors of the national economy with raw
materials, fuels and power. It includes smelting and processing of metals,
coking and coke chemistry, chemical materials and building materials such as
cement, plywood, and power, petroleum refining and coal dressing. (3)
Manufacturing industry refers to the industry that processes raw materials. It
includes machine building industry which equips sectors of the national
economy, industries of metal structure and cement products, industries
producing means of agricultural production, such as chemical fertilizers and
pesticides. According to the above principle of classification, the repairing
trades which are engaged primarily in repairing products of heavy industry are
classified into heavy industry while these engaged in repairing products of
light industry are classified into light industry.
Industrial
Enterprises above Designated Size
refer to industrial enterprises as legal person with annual business
revenue of over 20 million yuan.
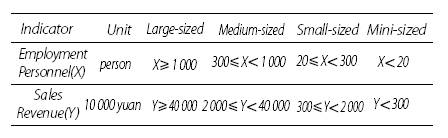
Large,
Medium, Small, Mini-sized Enterprises
Industrial enterprises are classified into
large, medium, small, mini-sized enterprises according to employment personnel
and sales revenue in accordance with the regulation of Classification of Large,
Medium, Small, Mini-sized Enterprises on Statistics in 2011. The standard of
classification as following:
Gross
Output Value of Industry��current price��
refers to total volume of final industrial products produced and
industrial services provided during the reporting period. It consists of 3
components: value of the finished products, income from processing for external
parties, and value of change in semi-finished products between the end and the
beginning of the reference period.
Total
Assets
refer to all resources formed by transaction or other activities, which
are owned or controlled by enterprises and expected to bring economic benefits
to the enterprises. Classified by the degree of liquidity(the
time of assets to be liquidated or consumed), total assets include working
capitals and immovable assets. Working capitals can be classified into monetary
assets, trading financial assets, notes receivable, accounts receivable,
advanced payments, other prepaid money and inventories. Immovable assets can be
divided into long-term equity investment, fixed assets, intangible assets and
other immovable assets.
Working
Capitals
the assets should be classified into working
capital if meeting one of the following conditions: (1) expected to be
liquidated, sold or consumed in one normal operating cycle, mainly including
inventory, account receivable, etc.; (2) owned for transaction purpose; (3)
expected to be liquidated in one year (including one year) since balance sheet
date; (4) cash or cash equivalent without limited ability of exchanging other
assets or paying debts in one year from balance sheet date, including monetary
funds, note receivable, accounts receivable, inventory and other items.
Fixed
Assets
refer to the physical assets owned over one
accounting year for the purpose of production, providing services, rent or
business management, including the use of more than one year of housing,
buildings, machines, machinery, transport equipment and other production and
business-related equipment, apparatus, tools, etc.
Revenue
from Principal Business
refers to revenues accepted by enterprises from the sales of products, labour services provided and etc. in the principal
business.
Cost
of Principal Business
refers to total costs for enterprises to operate the principal business.
Tax
and Extra Charges of Principal Business
refer to the tax and charges including the business tax, consumption tax,
city maintenance and construction tax, resources tax, land increasing value tax
and extra charges for education and etc. in the operation of principal
business.
Total
Pre-tax Profits
refer to the business results of enterprises in certain accounting
period, that is the profits gained from the revenues after deducting the costs,
which means the final achievements in the reference period. To the enterprises
implemented the Regulation of Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises in
2006, total pre-tax profits equals to business profit add non-operating revenue
and minus non-operating expenditures. To the enterprises not implemented, total
pre-tax profits equals to business profit add investment income, subsidies,
non-operating revenue and minus non-operating expenditures.
Total
Profits and Taxes
refers to the sum of the total profits, tax and extra charges of principal
business and the value added tax payable of industrial enterprises.
Proportion
of Products Sold
reflects the actual sale of industrial products, analyzing the
production-selling and supply-demand relations. It is calculated as:
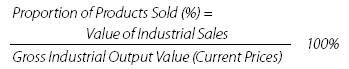
Ratio
of Total Assets to Industrial Output Value
reflects the profit-making capability of all assets of the enterprise and is
a key indicator manifesting the performance and management and evaluating the
profit-making potential of the enterprise. It is calculated as follows:
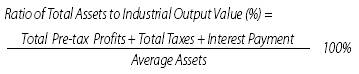
In the above formula, total taxes is the sum
of tax and extra charges of principal business and value-added tax payable; and
average assets is the arithmetic mean of the sum of beginning assets and ending
assets.
Ratio
of Debts to Assets
reflects both the operation risk and the capability of the enterprise in
making use of the capital from the creditors. It is calculated as follows:
![]()
Number
of Times of Turnover of Working Capitals
refers to the number of times of turnover of working capital in a given
period of time, which reflects the speed of the turnover of working capital of
industrial enterprises, and is calculated as follows:
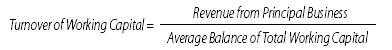
In the above formula, average balance of
total working capital refers to the arithmetic mean of the sum of circulating
funds at the beginning and at the end of the reference period.
Ratio
of Pre-tax Profits to Total Industrial Costs
refers to the ratio of profits realized in a given period to the total
costs in the same period, which reflects the economic efficiency of input cost
and is calculated as follows:
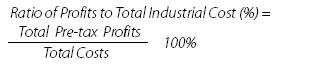
Total costs in the above
formula is the sum of cost of products sold,
marketing cost, management cost and financial cost.
Liquidity
Ratio
refers to the ratio of current assets and current liabilities, which is
used to measure the enterprise's ability to turn the current assets into cash
to repay its debts before the short-term debt maturity. It is calculated as
follows:
![]()
Quick
Ratio
refers to the ratio of quick assets and current liabilities, which is used
to measure the enterprise��s ability to turn the current assets into cash
immediately to repay its current liabilities. It is calculated as follows:
![]()