Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Percentage
of Graduates in Primary Schools Entering Junior Secondary Schools
refers to the proportion of school-age students in junior secondary
schools to the total number of junior school-age students.
Percentage
of School-age Children Enrolled
refers to the proportion of children enrolled at primary schools to the
total number of primary school-age children (including retarded children, but
excluding blind, deaf and mute children). The formula is:
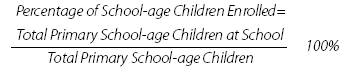
Network
Education
refers to the net education implemented by modern distance education
selected institute approved by the Ministry of Education, who recruit the
regular and adult undergraduate students and junior college students base on
Internet to give high level education.
Patent
is an abbreviation for the patent right and refers to the exclusive
right of ownership of the inventors or designers for the creation or
inventions, given from the patent offices after due process of assessment and
approval in accordance with the Patent Law. Patents are granted for inventions,
utility models and designs. This indicator reflects the achievements of S&T
and design with independent intellectual property.
Research
and Experimental Development (R&D)
refers to systematic and creative endeavor aimed at expanding the overall
volume of knowledge and applying the knowledge to invent new uses. It includes
basic studies, application research and experimental development. For
industrial enterprises, their R&D mainly belongs to experimental
development activities.
Basic
Research refers to empirical or theoretical
research aiming at obtaining new knowledge on the fundamental principles
regarding phenomena or observable facts to reveal the intrinsic nature and
underlying laws and to acquire new discoveries or new theories. Basic research
takes no specific or designated application as the aim of the research. Results
of basic research are mainly released or disseminated in the form of scientific
papers or monographs. This indicator reflects the innovation capacity for
original knowledge.
Applide Research refers to creative research
aiming at obtaining new knowledge on a specific objective or target. Purpose of
the applied research is to identify the possible uses of results from basic
research, or to explore new(fundamental)methods or new
approaches. Results of applied research are expressed in the form of scientific
papers, monographs, fundamental models or invention patens. This indicator
reflects the exploration of ways to apply the results of basic research.
Experiments
and Development refers to systematic activities
aiming at using the knowledge from basic and applied researches or from
practical experience to develop new products, materials and equipment, to
establish new production process, systems and services, or to make substantial
improvement on the existing products, process or services. Results of
experiment and development activities are embodied in patents, exclusive
technology, and monotype of new products or equipment. In social sciences,
experiment and development activities refer to the process of converting the
knowledge from basic or applied researches into feasible programmes
(including conduct of demons- tration projects for
assessment and evaluation). There are no experiment and development activities
in the science of humanities. This indicator reflects the capability of
transferring the results of S&T into technique and products, and measures
the realization of S&T in spearheading the economic and social development.
R&D
Personnel
refer to persons engaged in research, management and supporting
activities of R&D, including persons in the project teams, persons engaged
in the management of S&T activities of enterprises and supporting staff
providing direct service to the research projects. This indicator reflects the
size of personnel engaged in R&D activities with independent intellectual
property.
R&D
Personnel as Full-time Equivalent
refers to the sum of the full-time persons and the full-time equivalent of
part-time persons converted by workload. For instance, if there are 2 full-time
persons and 3 part-time workers (20%, 30% and 70% of working hours respectively
on R&D activities), the full-time equivalent are 2+0.2+0.3+0.7=3.2
person-years. This is an interna- tionally
comparable indicator of S&T manpower input.
Technology
Market
can be regarded narrowly as technical-dealings place where technique
transfer is made or technology-related good traded at certain time. As shown in
statistical datum presently, turnovers are resulting either from purchase or
from transfer of techniques, together with numbers related to the inquiry or
services involved in technologies.